ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Unit 1: Characteristics and Mindset of an Entrepreneur
Unit 2: Identifying Business Opportunities
Unit 3: Business planning and Market Research
Unit 4: Legal and regulatory considerations for Startups in each partner country
In this module you will find
INTRODUCTION
Aim & Competences
THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
Key concepts, background information, relevant theories
ACTIVITIES
Exercises, self-reflection & practical resources to promote inclusive e-learning
Glossary
Frequently used words of the module
USEFUL TIPS
Advice, ideas and proposals on relevant issues
INTRODUCTION

AIM
This module aims to:
- empower participants with the essential characteristics, mindset, and skills needed to become successful entrepreneurs. It focuses on recognising business opportunities, conducting market research, developing a comprehensive business plan, and understanding legal considerations for startups in partner countries. Through this training, women will be equipped to start and grow their own businesses, fostering economic independence and social empowerment.
Competences
Identifying business opportunities
Knowledge: analysing unmet needs, observing trends, assessing regulatory changes.
Skill: ability to assess market gaps, recognise consumer trends, and adapt ideas from other regions or industries
Attitude: encouraging participants to embrace change, think creatively, and seize upon emerging trends and market shifts.

Characteristics and Mindset of an Entrepreneur
Knowledge: essential characteristics and mindset required for entrepreneurial success.
Skill: decision-making skills, innovative thinking abilities, and strategic vision necessary for identifying opportunities.
Attitude: proactive and resilient attitude, instilling confidence, a willingness to learn from failure.
Business Planning and market research
Knowledge: comprehensive understanding of the components of a business plan, conducting a SWOT analysis.
Skill: create dynamic business, identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
Attitude: proactive and analytical mindset, adaptability
Legal and regulatory considerations
Knowledge: Different SME legal forms in each country
Skill: to navigate the legal landscape for start-ups
Attitude: empowering participants to make strategic decisions and effectively structure their businesses
UNIT 1
Characteristics and Mindset of an Entrepreneur
Unit 1
One of the major reference at EU level while talking about entrepreneurial skills at EU level is the EntreComp framework (see useful tools), which encompasses the 3 most important areas and 15 competences that an entrepreneur should have. Here is a summary of the main characteristics of an entrepreneurial mindset:
- Success orientation. Entrepreneurs have a great capacity for work and perseverance that they use to achieve the objectives they have set. It is important to remember that by achieving small objectives, achieving bigger goals will follow. If someone sets unattainable goals from the beginning, frustration and perhaps abandonment will appear.
- Independent and with initiative. It is unlikely to be a successful entrepreneur without initiative. How could we develop it? A good example is to promote habits that facilitate decision-making, especially in the most complicated moments.


The entrepreneur must be creative and innovative and be prepared to find the “competitive advantage” or “added value” that keeps his or her company in a good position in the market.
An entrepreneur must be a good leader, and that does not mean telling the employee what to do, but rather leading the team.
An entrepreneur must be aware not only of what he knows, but above all of what he needs to learn. An entrepreneur don´t think that he or she knows everything, there will always be someone or something that will teach them something new that will be useful for his or her business idea.
Analysing the company and the market from an overall view, attentive to any legislative, social or technological modification that may negatively or positively affect the company.
At any time, the market can change, and you must be able to adapt to the change, the survival of the business will depend on the flexibility of the entrepreneur. If an entrepreneur wants to adapt to change, he or she will surround themselves with creative people with varied training, study social trends, etc…
Almost all entrepreneurs have had to overcome failure at some point to achieve success. They can write down on paper the events that led to a failure so that you can avoid them in the future.
Be a good negotiator. The ability to maintain a smile and manage negative emotions during difficult negotiations and in the face of hostile people are key to obtaining the necessary support for the business.
Being consistent with the decisions they make, with their results, assuming their responsibilities and facing success with simplicity, thanking those who helped them along the way.
USEFUL TOOLS
Although many of the characteristics of an entrepreneur are innate, many of them can be worked on to be acquired with practice. Here is an example of some useful tools to improve the skills of an entrepreneur.
EntreComp: The Entrepreneurship Competence Framework.
The EntreComp framework presented in this report proposes a shared definition of entrepreneurship as a competence, with the aim to raise consensus among all stakeholders and to establish a bridge between the worlds of education and work.
https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC101581
MindTools: Entrepreneurship skills.
MindTools offers a wide range of resources and articles focused on developing entrepreneurial skills, including leadership, creativity, and resilience. It provides practical tips and techniques to enhance entrepreneurial mindset and effectiveness.
LinkedIn Learning
LinkedIn Learning offers a vast library of video courses taught by industry experts, addressing skills such as leadership, resilience, and emotional intelligence. Users can access courses like “Developing a Growth Mindset” and “Emotional Intelligence for Leaders,” equipping them with strategies to navigate challenges, manage emotions, and cultivate self-confidence in professional settings.
Trello
Trello is a productivity tool that helps users organise tasks and projects visually. By using Trello boards to plan and prioritise goals, users can develop a success-oriented mindset, take initiative in managing their tasks independently, and adapt to changes in priorities, ultimately building self-confidence in their ability to achieve their objectives.
Ideou
IDEOU offers online courses focused on fostering creativity, innovative thinking, and design leadership. Through courses like “Leading for Creativity” and “Design Thinking for Entrepreneurs,” participants learn practical methodologies and tools to enhance their creativity and adaptability in dynamic environments.
UNIT 2
Identifying Business Opportunities
UNIT 2
Examples of effective systems for searching business opportunities:
- Identify unmet needs. There are many unmet needs in a community that can be seen by an entrepreneur as an opportunity, for example, opening a kindergarten in a newly built neighborhood, the vast amount of the population would be young parents in need of childcare.
- Observation of trends. As an example of trend observation, sportswear manufacturers who began by advertising clothes primarily for sports participation, then observed that young people also wore them during the day and not only when doing sports.
- • Hobbies. Many people manage to turn their hobbies into ideas for their business, expanding ideas to suit their clientele.

- Changes in legal regulations. Many new companies have been set up because of new regulatory changes, such as companies related to environmental issues, climate change and the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Observation of other people’s deficiencies. Deficiencies in the competition can always be seen as an opportunity for the entrepreneur. Many companies, for example, have capitalised on the advertising efforts of large food delivery services to sell similar products in towns where larger companies do not offer delivery.
- Factors of demographic and social change. Studying the countries situation where the business will be developed and understanding the surrounding population is crucial.
- Consumer trends as business ideas. As we have mentioned, one of the most effective methods of detecting new business opportunities is undoubtedly the observation of new consumer trends; consumers modify their preferences in everyday matters.
- Adapt ideas that come from abroad. Many of the businesses that are set up today come from other countries. The formula of being inspired by a business that has already been successful outside our borders is one of the most interesting options when it comes to innovating in our market and it has many advantages.
- The new sources of employment. The labour market is constantly evolving due to various factors such as economic recovery, technological innovation, internationalisation, globalisation, and climate change. These changes create numerous new opportunities for employment and business generation.
USEFUL TOOLS
To know how to identify new business opportunities is an important value to each entrepreneur, here is a list ofsome interesting tools: Google Trends offers insights into emerging search trends, helping users spot potential market gaps. Trend Hunter provides curated trend reports across industries, aiding in staying ahead of the competition. Mintel offers in-depth market research and analysis, enabling users to validate ideas and make informed decisions. Quora fosters engagement with a community of experts, facilitating the identification of consumer needs and emerging trends. Crunchbase offers data on startups and funding, assisting in the discovery of potential collaborators and disruptive opportunities.
Trend Hunter
Trend Hunter is a platform that curates trend reports and insights across various industries. By exploring innovative ideas and emerging trends, users can identify new business opportunities and stay ahead of the competition in rapidly evolving markets.
Mintel
Mintel is a market research firm that provides insights and analysis on consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes. By accessing Mintel’s reports and data, users can identify business opportunities, validate ideas, and make informed decisions for their ventures.
Quora
Quora is a question-and-answer platform where users can ask questions, share knowledge, and engage in discussions on various topics. By participating in relevant discussions and observing user inquiries, entrepreneurs can identify consumer needs, pain points, and emerging trends that may lead to business opportunities.
Crunchbase
Crunchbase is a platform that provides information on startups, investors, and funding rounds. By exploring Crunchbase’s database, users can discover emerging startups, innovative business models, and investment trends, helping them to identify potential opportunities for collaboration or disruption.
Google Trends
Google Trends allows users to explore the popularity of search queries over time and in different regions. By analysing search trends, users can identify emerging topics and interests, helping them to spot potential business opportunities and consumer trends.
UNIT 3
Business planning and Market Research

The business plan is an instrument in which each of the areas that determine business activity are developed. This document requires an entire planning and analysis process to detect the viability of the business idea, making it a dynamic and modifiable document. Since the company is immersed in a changing environment and affected by external variables that happen abroad.
For a business plan to be complete it had to answer the following questions:
- Technical feasibility, can it be done?
- Economic feasibility, will it give the expected results?
- Financial feasibility, do the necessary resources exist?
Within the marketing plan, an analysis of the competition must be carried out to find the strengths and weaknesses and determine what strategies to follow to make the most of them. The objective of this section is to identify the type of competitive advantage that the company has.
SWOT analysis is the main instrument available to analyse the market and competition, where a distinction is made between strengths and weaknesses (internal aspect) and opportunities and threats (external aspect).
- Strengths. Strengths that the company must position itself against the competition.
- Opportunities. It is one of the external factors to the project, and is made up of each of the opportunities offered by the sector in which the product will be marketed, such as a lack of competition, etc.
SWOT analysis is the main instrument available to analyse the market and competition, where a distinction is made between strengths and weaknesses (internal aspect) and opportunities and threats (external aspect).
- Weaknesses. Vulnerable points that the company has compared to the competition. When analysing the business idea, it is possible not only to be aware of the weaknesses, but at the same time to look for possible alternatives and solutions to solve them.
- Threats. They are all those external factors that can negatively influence and condition the marketing of the product. At this point, factors such as entry barriers (such as fiscal or legal restrictions) or macroeconomic factors such as the possibility of increasing interest rates if a large volume of financing is necessary must be considered.
Useful Tools
The business plan, SWOT analysis and marketing plan are essential tools that every entrepreneur must develop on their business idea. In addition, these must be constantly changing and updated in line with current legislation, and in keeping with the internal and external changes that constantly occur in the company.
Creately: 30 SWOT analysis template
SWOT analysis examples and templates can be modified online using this tool. After editing you can export it and include them in PowerPoint presentations(PPT), Word documents, Excel files or any other document critical to you.
30+ SWOT Analysis Templates and Examples for Any Situation
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas was proposed by Alexander Osterwalder based on his earlier book: Business Model Ontology. It outlines nine segments which form the building blocks for the business model in a nice one-page canvas. You can find a detailed explanation in his bestselling book “Business Model Generation
Sustainable Business Model Canvas
The Sustainable Business Model enriches the original Business Model Canvas with 3 additional sections: A list of sustainable Goals, negative externalities, positive externalities
Strategy: Customer/ Strategy/ Resource Matrix by Hooley
This framework is designed to assess the attractiveness of a market segment before deciding which market to target.
Analyze: Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Porter’s five forces analysis has proven a useful strategic planning toolin both business and market-based planning, especially when it comes to understanding the level of competitive intensity within the industry.
https://creately.com/usage/strategic-planning-tools-templates/
UNIT 4
Legal and regulatory considerations for Startups in each partner country
In this unit we will see the different Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Startups in the countries to which the partners of this project belong:
- Spain
- France
- Greece
- Italy
- Ireland
Unit 4
There is different legal entities in Spain to create an SME, the most common are:
- Individual self-employed: The legal form is centered around the entrepreneur where no actual SME is created, and the VAT number is the same as the personal ID. It is commonly used in the retail sector and small businesses where only the entrepreneur works in the company.
- Legal company as S.L (Limited Society): This can be established with a single owner (unipersonal society) or with multiple owners. Currently, it is the most common legal form and can be created electronically within 48 hours.
- Work Cooperative: This is a more social form of business where the workers are also the owners of the company. The board belongs to the workers as an assembly.
- When choosing the legal form of a company, several factors need to be considered, such as the number of partners, the amount of money paid into the share capital, the social or tax status of the director, and the extent of liability.
- Below you will find a table gathering information about the main types of company.

To start a business in Greece of any legal form, you need to have an active Greek Tax Identification Number (VAT) and use the login details for the TAXIS system. If you are a European citizen, you will need to obtain a Greek VAT number remotely via videoconference and you will also need to fill in a digital form and make a telephone appointment with a representative of the Independent Authority for Public Revenue (AADE). You can find out more here. Here are the available legal types and their respective laws:
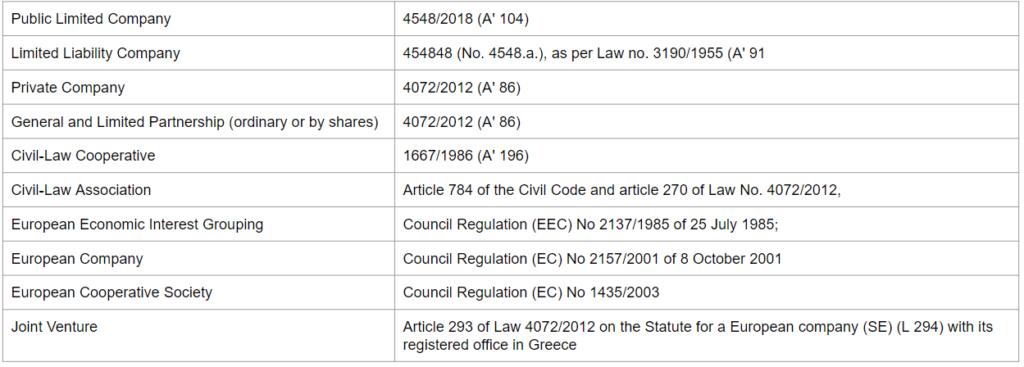
Unit 4
To set up a company, various bureaucratic actions must be undertaken which include the activation of one of the various corporate forms made available by Italian law. This type of decision depends on various factors such as business risk, the number of shareholders or the impact on personal assets. The Italian state recognizes different types of entrepreneurial forms, but the small and medium-sized entrepreneur chooses from the following:
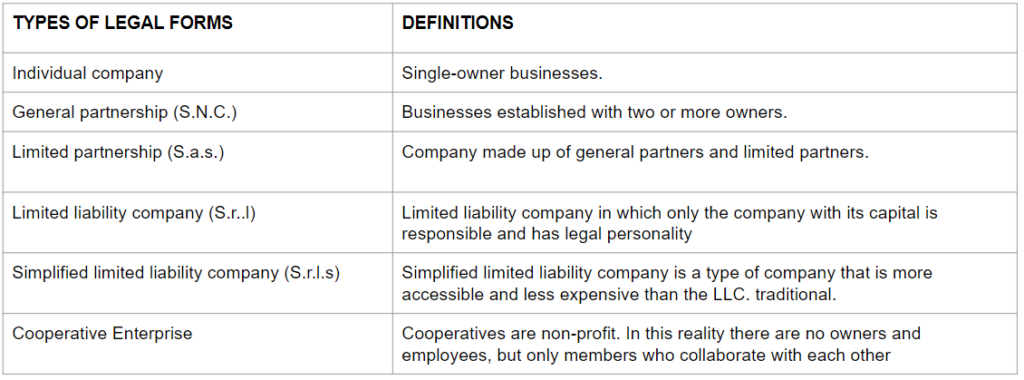
In Ireland, businesses should register their name with the Companies Registration Office (CRO). There are different legal structures for businesses which determine the taxes that must be paid and the personal liability for business debts. Additionally, businesses must charge VAT on the sale of their goods and/or services. There are several funding opportunities and grants that new, start-up businesses can apply for, e.g., through Enterprise Ireland (Citizens Information, 2023).

Unit 4
Useful Tools
To know the legal and regulatory consideration for startups is an important starting point, depending on the nature of the business, the required investments and the projected annual income, one legal form may be more suitable than another. Here are various country-specific tools to help determine the best legal form for your to be done, or the annual incomings it´s better to use one or another legal form for your business.
Useful Tools
Plataforma PYME
The choice of legal form will depend on a series of factors, such as the number of partners, the amount of share capital and liability to third parties; whether the activity is carried out with a physical establishment or not, etc. The Spanish government, through Plan Pyme, makes available a very simple tool to choose the legal form of a company.
https://plataformapyme.es/es-es/herramientas-digitales/Paginas/formas-juridicas.aspx

Entreprendre - Service public
The government is offering a summary of all the legal forms that a company can take, as well as a directory listing the key contacts for entrepreneurs in the various regions.
ESPA
The new “Regional Development Partnership 2021-2027” (“ESPA 2021-2027”) largely reflects the new priorities of the European Commission and the new development priorities of Greece for the coming years.
The projects/actions to be funded by the new ESPA take into account the specific conditions and needs of the country in the coming years and respond to the structural shortcomings of the Greek economy.
SNI - Servizio Nuove Imprese - Unioncamere
The platform of Unioncamere offers different dimensions of use, which aim to accompany the user on a path of awareness on the meaning of becoming entrepreneurs and doing business, sharing basic information, entrepreneurship orientation, technical expertise, training activities and technical assistance for creation of business, news and information from the territories, made available by the Italian Chamber of Commerce network.
Support SMEs
As part of the Irish Government’s Supporting SMEs campaign, this online tool was developed to help Irish start-ups and small businesses identify a range of government agency supports that exist. This online tool offers advice related to the following topics: Start-ups; Digitisation; Climate and Energy; Access to Finance; Exporting and Scaling.
KEY TAKE AWAY
Women facing barriers to financial independence must engage with the essential skills and knowledge needed to start their own eco-enterprises. This involves instilling the characteristics and mindset of successful entrepreneurs, such as a strong orientation towards success, independence, creativity, leadership, and adaptability. Identifying business opportunities through market observation, trend analysis, and recognising unmet needs is important. Furthermore, understanding the importance of comprehensive business planning, market research, and legal considerations is essential for the viability and sustainability of the venture.

the EntreComp framework is set to become a reference de facto for any initiative aiming to foster entrepreneurial capacity of European citizens
A strategic planning tool used to identify Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a business venture or Project
The process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, including its size, trends, competitors, and consumer preferences, to inform business decisions.
REFERENCES
- Bacigalupo M, Kampylis P, Punie Y and Van Den Brande L. EntreComp: The Entrepreneurship Competence Framework. EUR 27939 EN. Luxembourg (Luxembourg): Publications Office of the European Union; 2016. JRC10158. https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC101581
- Aguado Carretero, Pilar. The Guide of the entrepreneur. From the idea to the business. Published in paper by Bancaja Foundation, Spanish Edition; 2009 and posterior editions.

Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor EACEA can be held responsible for them.
